Audio Check: Your Guide To A Flawless Podcasting Experience

 Jul 9, 2025
Jul 9, 2025
 Podcast
Podcast
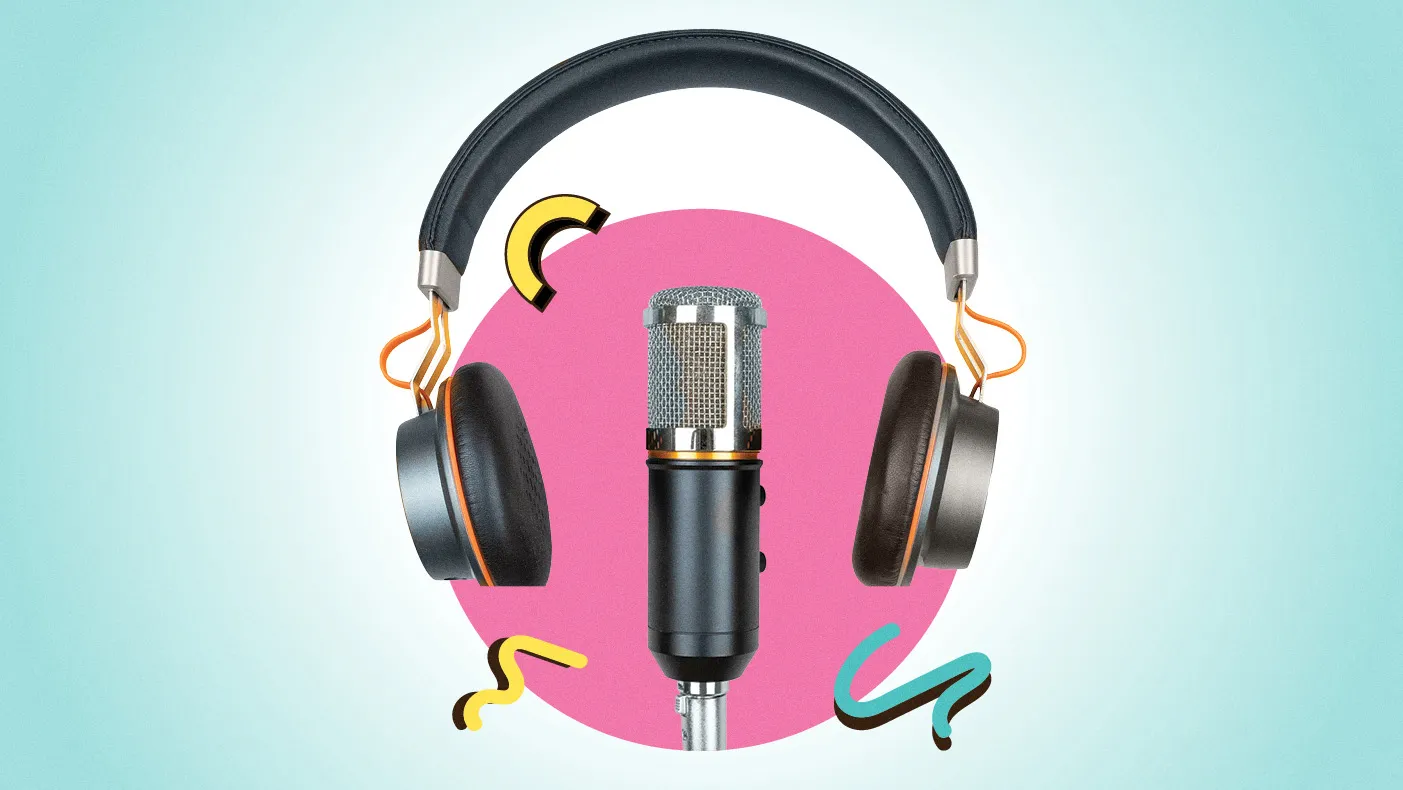
No one disputes that clear audio is one of the cornerstones of an engaging podcast experience. While content is king, the way that content is delivered—especially through sound—can make or break your podcast’s success. Listeners place great value on hearing high-quality sound recordings before they decide to continue tuning in. That’s why your audio must remain professional, polished, and easy on the ears.
In today’s blog, we will walk you through essential tips and techniques to help you create amazing audio for your podcast, whether you're just starting or looking to level up your production.
1. Quality of Microphones
The microphone is the heart of your podcasting setup. Investing in a good quality microphone is crucial because it captures the full range and richness of your voice. A low-end mic may pick up static, echo, or background noise, while a higher-end mic provides cleaner, more accurate sound reproduction. Consider USB mics for ease of use, or XLR mics if you’re working in a more professional setup. Choose a microphone that complements your voice and works well in your specific recording environment.
2. Room Acoustics
The room you record in plays a major role in how your audio turns out. Large, empty, or reflective spaces can cause echo and reverb that muddle your sound. Try to record in a smaller, carpeted room with minimal hard surfaces. Adding soundproofing foam panels, curtains, or rugs can significantly improve the acoustics. Even a makeshift setup like recording in a closet full of clothes can yield surprisingly good results.
3. Background Noise
Background noise is one of the most common enemies of clear podcast audio. From air conditioners and computer fans to outside traffic and barking dogs, unwanted sounds can creep into your recordings easily. Before you hit the record button, take a moment to identify and eliminate as much of the ambient noise as possible.
During post-production, use noise reduction tools in your editing software to clean up any residual background hums or hisses. These tools can make a huge difference without altering your voice's natural tone.
4. Gain Levels
Proper gain settings are essential. Gain controls the input level of your microphone before it is recorded. If it’s set too low, your voice will be barely audible; too high, and it will clip and distort. A general rule of thumb is to aim for your voice to peak around -3 to -6 decibels. Monitor your levels using audio meters while recording, and adjust as needed to maintain balance and clarity.
5. Equalization (EQ)
EQ is a powerful tool that helps shape the tone and clarity of your voice. It works by adjusting specific frequency ranges. For example, boosting the mid-range can make your voice more present, while reducing lower frequencies can remove muddiness. Every voice is different, so experiment with EQ settings to find the best sound for you. A subtle touch can enhance your vocal presence without sounding unnatural.
6. Audio Compression
Audio compression is used to smooth out the dynamic range of your audio. In simple terms, it ensures that the quiet parts of your voice are audible and the loud parts aren't jarring to listeners. A well-compressed track is consistent in volume, making for a more pleasant listening experience. Don’t overdo it, though—too much compression can make your audio sound flat or robotic.
7. Controlling Sibilance
Sibilance is the high-pitched “s” or “sh” sound that can be unpleasant and piercing to listeners. This can occur naturally depending on how you speak and the sensitivity of your microphone. To control this, use a de-esser, which is a plugin or tool that automatically reduces harsh sibilant frequencies (typically around 5-7kHz). Alternatively, you can manually adjust these frequencies during editing to soften the impact.
8. Background Music
Adding background music can enhance your podcast’s mood and branding, but it must be handled with care. Ensure that any music you use is licensed for your podcast and that it doesn’t overpower your voice. The music should complement your speech, not compete with it. Use volume automation to duck the music under your voice and bring it back up between segments or at the end.
9. File Format and Audio Quality
Choosing the right file format and bitrate matters. For distribution, MP3 is commonly used due to its smaller file size and compatibility, but always export at a high bitrate (at least 128 kbps, ideally 192 or 256 kbps). If you're archiving your podcast or editing it further down the line, use WAV format for lossless audio quality. This ensures the best possible preservation of your original recording.
10. Editing
Editing is where your podcast comes together. With tools like Audacity, Adobe Audition, GarageBand, or Reaper, you can easily trim silences, remove mistakes, clean up background noise, and apply EQ and compression. Editing is not just about making things sound good—it’s about crafting a professional, listenable experience that respects your audience’s time and attention.
11. Test on Multiple Devices
After editing, don’t forget to test your podcast on various playback devices like headphones, car speakers, laptop speakers, and smartphones. Each will sound slightly different, and you want to ensure your audio is balanced across them all. If your podcast sounds too bass-heavy on one or too tinny on another, go back and make minor adjustments.
Conclusion
Producing a podcast with flawless audio may seem daunting at first, but with the right equipment, techniques, and attention to detail, anyone can achieve professional-sounding results. High-quality audio is not just a bonus—it’s a necessity for engaging and retaining listeners. Whether you're a seasoned podcaster or a newcomer to the field, taking the time to refine your audio will set you apart in an increasingly crowded space. Happy podcasting!
